Plugin Signing
Plugin Signing is a mechanism introduced in the 2021.2 release cycle to increase security on the JetBrains Marketplace and all IntelliJ-based IDEs.
The JetBrains Marketplace signing process is designed to ensure that plugins are not modified over the course of the publishing and delivery pipeline. If the author does not sign the plugin or has a revoked certificate, a warning dialog will appear in the IDE during installation.
On our side, we will check if the public part of a key is present, and we will verify the signature. This is similar to the Google upload key mechanism.
How Signing Works
To be sure a file has not been modified, the file will be signed twice – first by the plugin author, then by JetBrains Marketplace.
Signing and Verification Process
The plugin author generates a key pair and uploads the public part to JetBrains Marketplace (not available yet).
A build tool signs the plugin distribution file during the assembly process.
The user uploads the plugin distribution file to the JetBrains Marketplace.
JetBrains Marketplace checks if the public key is present in the user's profile.
JetBrains Marketplace verifies the signature.
The JetBrains signing and verification process is as follows:
JetBrains CA is used as the source of truth.
Its public part will be added to the IDE's Java TrustStore, while the private part is used only once to generate an intermediate certificate.
The private key of the JetBrains CA is supersecret; in fact, we've already said too much.
The intermediate certificate issues a certificate that will be used to sign plugins. This way, it will be possible to re-generate this certificate without access to JetBrains CA's supersecret private key. The private key of the intermediate certificate is issued and kept in the AWS Certificate Manager, and no application has access to it; people's access is also limited. So now we have an AWS-based Intermediate CA. The public part of the intermediate certificate will be added to the plugin distribution file together with the signing certificate.
The certificate used to sign plugins is stored securely, too. JetBrains Marketplace uses AWS KMS as a signature provider to sign plugin distribution files.
Signing Methods
For signing, the Marketplace ZIP Signer library is used. For Gradle-based projects, it can be used conveniently using the provided tasks via Gradle Integration. Alternatively, a standalone CLI Tool can be used.
Both methods require a private certificate key to be present.
Generate Private Key
To generate an RSA private.pem private key, run the openssl genpkey command in the terminal, as below:
After that, it's required to convert it into the RSA form with:
At this point, the generated private.pem content should be provided to the signPlugin.privateKey property (2.x, 1.x). The provided password should be specified as the signPlugin.password property (2.x, 1.x).
As a next step, we will generate a chain.crt certificate chain with:
The content of the chain.crt file will be used for the signPlugin.certificateChain property (2.x, 1.x).
Gradle Integration
IntelliJ Platform Gradle Plugin (2.x)
The IntelliJ Platform Gradle Plugin (2.x) provides the signPlugin task, which will be executed automatically right before the publishPlugin task when signPlugin.certificateChain and signPlugin.privateKey properties are specified. Otherwise, it'll be skipped.
See intellijPlatform.signing for configuration reference.
Configuration using Files
Instead of using the signPlugin.certificateChain and signPlugin.privateKey properties which expect the certificate chain and key to be provided directly, it's also possible to specify the paths to the files containing the certificate chain and key content. Use signPlugin.certificateChainFile and signPlugin.privateKeyFile properties instead.
Gradle IntelliJ Plugin (1.x)
The Gradle IntelliJ Plugin (1.x) provides the signPlugin task, which will be executed automatically right before the publishPlugin task when signPlugin.certificateChain and signPlugin.privateKey properties are specified. Otherwise, it'll be skipped.
An example signPlugin task configuration may look like this:
Using Files
Instead of using the signPlugin.privateKey and signPlugin.certificateChain properties which expect the key and certificate chain content to be provided directly, it's also possible to specify the paths to the files containing the key and certificate chain content. To do that, use the signPlugin.privateKeyFile and signPlugin.certificateChainFile properties instead.
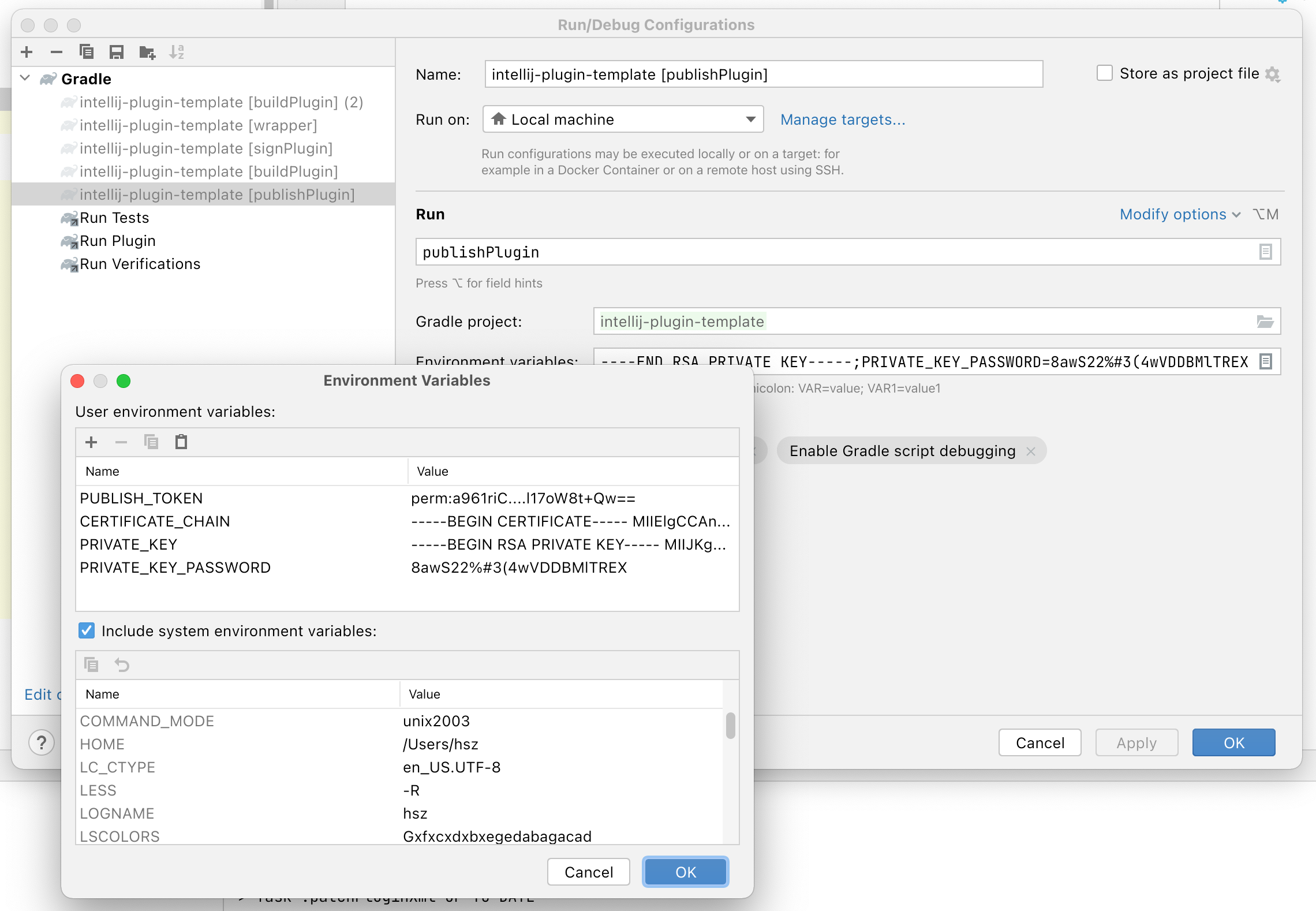
Provide Secrets to IDE
To avoid storing hard-coded values in the project configuration, the most suitable method for local development would be using environment variables provided within the Run/Debug Configuration.
To specify secrets like PUBLISH_TOKEN and values required for the signPlugin Gradle task (2.x, 1.x), modify your Gradle configuration as follows:
In the Run/Debug Configuration for publishPlugin Gradle task (2.x, 1.x), provide Environment Variables using relevant environment variable names:
CLI Tool
CLI tool is required if you don't rely on either Gradle plugin – i.e., when working with Themes.
Get the latest Marketplace ZIP Signer CLI Tool version from the GitHub Releases page. After downloading the marketplace-zip-signer-cli.jar, execute it as below:
Signing for Custom Repositories
Signing plugins hosted on a Custom Plugin Repository can be achieved for added trust between the repository and installation. However, unlike JetBrains Marketplace, the custom repository will not re-sign the plugin with the JetBrains key. Instead, a trusted private CA or self-signed certificate can be used to sign and validate plugins.
Verification
Before looking at how we can sign a plugin, let's first review how verification works when a non-JetBrains certificate is used. As of 2021.2, during verification, IntelliJ-based IDEs check if the plugin was signed with the JetBrains CA certificate or any public key provided by the user via . In 2021.2.1, a system property has been added: intellij.plugins.truststore, pointing to a trusted JKS TrustStore. During verification, the plugin's public key is extracted from the signature. The last certificate entry in the chain matched against the certificates stored in one of the storages from above.
Using a Trusted Internal CA
If an internal CA is available, it can be used to generate certificates for signing. When choosing this route, the certificate chain includes the root CA public key at the end of the chain.
With this approach, existing internal TrustStores may exist and could be used. Be sure when choosing a TrustStore that the CAs are limited to the internal CAs you trust. Using a TrustStore with public CAs can expose users to an attack vector.
If adding a TrustStore to a user's environment is not possible, the user may also add the root CAs public key to .
Using Self-Signed Certificates
Using a self-signed certificate is an option if no internal CAs exist. To generate the key and public key, see Generate Private Key.
If providing users with a TrustStore, you can generate one with the public key using keytool:
(note: the TrustStore password must remain changeit)
Otherwise, users may add the public key manually to .
Plugin Signature Verification
The signature of a plugin can be verified using the verifyPluginSignature Gradle task (2.x, 1.x).
By default, it will use the same certificate chain as provided to the signPlugin Gradle task (see Gradle Integration).
To verify the signature using the CLI tool, execute the verify command as below: